Around 110 million tons of fiber were processed world-wide in 2024, mainly for clothing, technical textiles and home textiles. Fiber consumption is growing – along with the world’s population and disposable income – on average between two and three percent per year. It is estimated that it will reach around 140 million tons by 2030.
Textile Market and Spinning Process
Yarn production
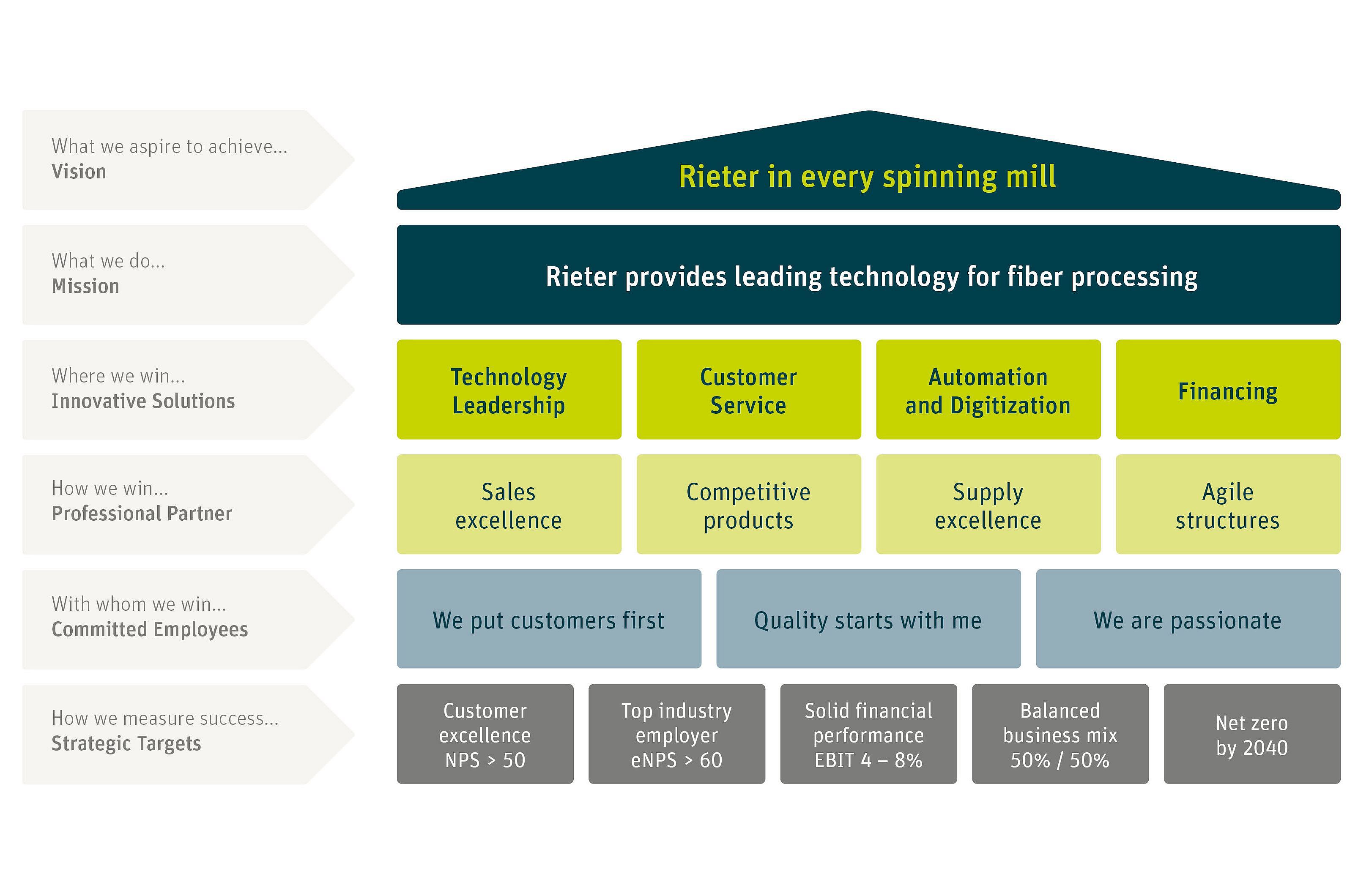
Rieter is the only systems provider that covers the complete manufacturing process in spinning mills: from fiber preparation through to the four end-spinning technologies.
The process from fiber to textile begins with fiber production. A yarn is produced from the fibers; for example, from cotton, linen, polyester or viscose. A textile is then produced from the yarn via various processing steps, such as weaving, knitting, dyeing or finishing.
Yarn manufacturing is a highly technological step in the textile value chain and can heavily influence the performance of downstream process steps.
Yarn is basically produced in two ways. The first method is by spinning staple fibers with a length of either 23 to 60 mm (short-staple fibers) or of more than 60 mm (longstaple fibers).
Yarn manufacturing can heavily influence the performance of downstream process steps.
The second method is by processing filaments to make continuous filament yarn. The yarns resulting from filaments have different properties from those produced from staple fibers. In the clothing industry, the yarn produced from staple fiber predominates because it offers pleasant wearing comfort.
The two types of yarn production each account for about 50 percent of world fiber consumption. Rieter is mainly engaged in yarn production from staple fibers. The most important staple fibers in 2024 were cotton (about 25 million tons), polyester (about 19 million tons) and viscose (about seven million tons). Cotton is a slow growing product due to natural limitations, but production of viscose and polyester is projected to grow in the coming years.
The process for producing a yarn from staple fibers consists of three stages: fiber preparation, spinning preparation and end spinning.
Fiber and spinning preparation

The fibers, which are delivered in bales, are separated, cleaned if necessary, and aligned. This takes place during opening and carding. Spinning preparation involves the homogenization and drawing of the sliver, and the machine used for this is known as the draw frame. In cotton processing, the comber also plays a role: here, short fibers are combed out in order to produce a higher quality yarn. By the end of the spinning preparation stage, a uniform sliver or roving has been produced.
Spinning process
In the end-spinning stage, the fiber mesh is further drawn (up to about 40 fibers in cross-section for very fine yarns) and spun into a yarn by twisting. Twisting takes place by means of a rotating spindle (ring spinning, compact spinning), by rotation of a rotor (rotor spinning) or by an air flow (air-jet spinning). Compact spinning is a variant of ring spinning that uses an auxiliary device to achieve yarn with a higher density as a result of improved fiber integration.
Winding
After spinning, imperfections are removed from the yarn. The yarn is then wound on a package to present it in a suitable form for the subsequent process steps in the textile production chain.
The winding machine serves as the final quality assurance in the ring spinning and compact-spinning process, and is crucial in the performance of the following steps. Yarn faults that are not detected here can result in machine downtimes during downstream processing, problems during the dyeing process, or faults in woven or knitted fabric.
Measured variables for capacity
Production of yarn from staple fibers is measured in spindle equivalents, with the production capacity of a ring spindle serving as the basis. The spinning unit of a rotor spinning machine corresponds to the productivity of five to six ring spindles, whereas that of an air-jet spinning machine corresponds to the productivity of 20 ring spindles.
A total of more than 250 million spindle equivalents worldwide were used in 2024 to produce yarn from the roughly 60 million tons of staple fibers, with about 94 million in China, 63 million in India, 72 million in Asian countries (excluding China, India and Türkiye) and 14 million in Türkiye. Every year, between 9 and 16 million spindle equivalents are installed on average.
Rieter delivered 0.83 million spindle equivalents in 2024 (2023: 2.31 million). In addition, spinning mills require consumables, wear & tear and spare parts for ongoing operation.
2024 yarn production figures
- 0
million tons of staple fibers processed
- 0
million spindle equivalents in use worldwide
- 0
million spindle equivalents delivered by Rieter
Textile Market
The world market for staple fiber machines relevant to Rieter has an annual volume of CHF 2 200 million to CHF 4 000 million. Rieter is the market leader with a share of about 30 percent.

Business with new machines, consumables, wear & tear and spare parts
The business with new machines is cyclical. The tendency to invest in the spinning industry is mainly influenced by expectations of fiber consumption and the margins that can be achieved through sale of yarns.
Fiber consumption is dependent on the economy, while the margins for yarn depend on the movement of raw material prices, capacity utilization, production costs of the spinning mills and foreign exchange rates. Government programs also have an influence.
Rieter aims to balance out the cyclicality of the machines business with consumables, wear & tear and spare parts, and after-sales services. This less cyclical business is driven by the degree of capacity utilization of operational spinning mills, which require consumables, wear & tear and spare parts.
Product and service offering

Rieter plans spinning mills, develops, produces and supplies the machines for fiber preparation, spinning preparation and end spinning, and supervises the installed machines throughout their life cycle. The company’s vision is to automate and digitize the complete value stream of the spinning process, making it more resource-efficient and improving performance.
Rieter, with all its brands, is established worldwide as a premium supplier. Innovative products and services from Rieter enable spinning mill owners to be more competitive. Success factors are low yarn production costs, which are achieved through savings on raw materials, energy, labor and productivity advantages. This enables sustainable yarn production or the production of special yarns that can be used to achieve higher prices.
The professionalism and availability of the service is also a key aspect when customers decide to buy Rieter solutions.